|
|
|
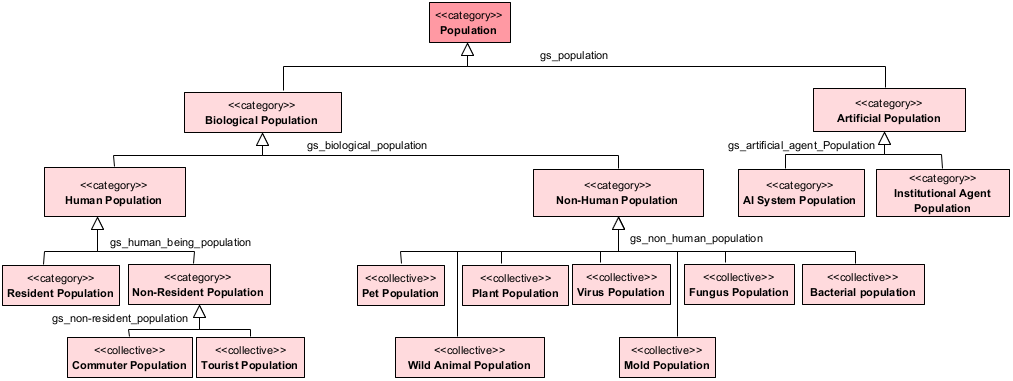
Class Diagram - Ontology of Population
![]() link
link
| Jump to: |
|
| Model Elements |
| Name | Description | ||
|
|
‘AI system’ means a machine-based system that is designed to operate with varying levels of autonomy and that may exhibit adaptiveness after deployment, and that, for explicit or implicit objectives, infers, from the input it receives, how to generate outputs such as predictions, content, recommendations, or decisions that can influence physical or virtual environments.
Source: https://artificialintelligenceact.eu/article/3/ |
||
|
|
Artificial Population is all populations that do not encompass natural beings (humans or not) and are designed by human beings. For instance, autonomous systems, institutional agents, intelligent artificial agents, etc. |
||
|
|
It is the collective of bacteria of a specified gender and species. A bacterial colony may expand in a geometric or exponential fashion. |
||
|
|
Biological Population is a group of biological organisms living in the same place at the same time. |
||
|
|
It is a collective of people who regularly travel some distance to work or study. |
||
|
|
It is a collective of Fungus, which is any of about 144.000 known species of organisms of the kingdom Fungi, including yeasts, mildews, molds, and mushrooms. | ||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
It is a subtype of the Biological Population collective, covering the subtypes of resident, non-resident populations in a given space and at the same time. |
||
|
|
It is a collection of fictitious persons that exist in the legal system, which are entities such as corporations, firms (business entities), and some government agencies. They are treated in law as if they were persons, i.e. they can do the things that a human person can normally do in law - such as make contracts, sue and be sued, own property, and so on. There are no natural persons (human beings) in this category. |
||
|
|
It is the collective of mold, a subtype of fungus that grown indoor. |
||
|
|
Non-Human Being Population is all populations that do not encompass human
beings but it is natural. It is subcategorized as: 2.1) Pet Population,
2.2) Wild Animal Population, 2.3) Plant Population, 2.4) Mobile Genetic
Element Population (MGE), 2.5) Fungus Population, 2.6) Protist Population,
and 2.7) Bacteria Population.
There is a subtype of MGE, which is the Virus Population. Also, there is a subtype of Protist Population, which is Mold Population. |
||
|
|
It is the collective of individuals who are not registered with the Registry of the Resident Population in a given municipality in a given time. It can be a tourist or a person who is temporally living in a particular place without the duties and rights of the residents. |
||
|
|
It is a collection of any domesticated or tamed animal that is kept as a companion and cared for affectionately. |
||
|
|
It is the collection of plants per unit area of land. Plant populations are characterized by their size (or density) and their structure (the number of individuals of different ages and sizes). |
||
|
|
It is a collection of Agents (biological or artificial) of the same taxonomic class, counted or sampled at a given location or area, given a time interval. |
||
|
|
It refers to the collective of people enlisted with the Resident
Population Registry in a particular local authority area in a given
time. The classification of a Resident Person as a <<role>> derives from
residency being an incidental characteristic of a human being. |
||
|
|
It is a collective of people who is traveling or visiting a place for pleasure or interesting. |
||
|
|
It is a collective of a kind of virus. It is possible that viruses originated from mobile genetic elements that acquired intercellular migration capabilities. They could be descendants of formerly free-living organisms that adopted a parasite replication strategy. |
||
|
|
Urban wildlife animal populations consist of species that utilize human-dominated ecosystems. |
||