|
|
|
Risk-driven Ontology of Urban Systems - complemento : Package . Hazardous Situation : Class . Urban System at Risk : Class (in Risk-driven Ontology of Urban Systems / Ontology of Urban System / Fragment_OntologyOfUrbanSystemAtRisk / Fragment_RiskDriverAndObjectAtRisk / Ontology of Exposure / Risk-driven Ontology of Urban Systems - complemento)
Class Diagram - Ontology of Urban System
![]() link
link
| Jump to: |
|
| Model Elements |
| Name | Description | ||
|
|
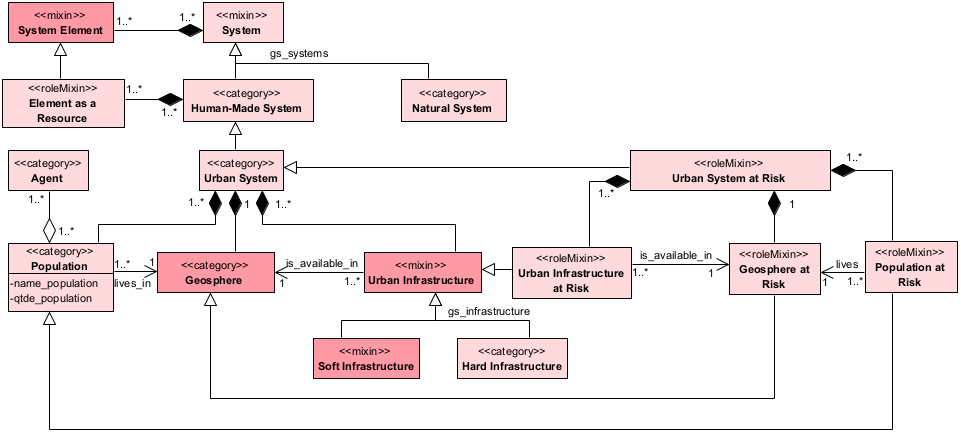
Any agentive Object, either physical (e.g. a person, a robot, an oak), or social (e.g. a corporation, an institution, a community). Defined by: https://w3id.org/italia/onto/l0 |
||
|
|
It
is everything that is used to satisfy the human needs. |
||
|
|
The geosphere is the collection of physical and geological elements that contribute to shaping the Earth's surface. In the urban environment, the geosphere provides the foundation upon which population and infrastructure develop so that the elements of the geosphere affect them, but the population and infrastructure can also modify the geosphere. For example, urban development and even risk mitigation often involve excavations that interact with and often modify the underlying geology. Therefore, urban development requires an understanding of the local geology, such as soil stability, groundwater conditions, and subsurface characteristics. The geosphere includes the following elements: subsurface, soil, topography, resources, and hydrology. |
||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
It is the built environment, the physical connections between places that move people, materials, information, and energy. These "fixed" things include roads, railroads, pipes, buildings, cables, and the networks composed of these constructions. Moreover, encompasses the green infrastructure, which is a category of ecological-oriented designed structures, i.e., a combination of grey and green infrastructures; and the Blue Infrastructure defined as the blue areas, a mix of natural resources (rivers, sea, beaches, etc) and human-designed elements. |
||
|
|
A system designed by human beings. | ||
|
|
It is a set of elements that arise naturally, without human construction. |
||
|
|
It is a collection of Agents (biological or artificial) of the same taxonomic class, counted or sampled at a given location or area, given a time interval. |
||
|
|
It is a collection of Agents (biological or artificial) of the same taxonomic class, counted or sampled at a given location or area, given a time interval that is at risk. |
||
|
|
Soft infrastructure refers to the intangible things needed to maintain or improve the utilities and services such as financial, health, cultural, and social in an urban system. The population uses the infrastructure of an urban system through services offered by public or private agents. | ||
|
|
A set of things working together as parts of a mechanism or an interconnecting network; a complex whole.
In Return Project, in the ontological model, a system is categorized as 1) made by humans (artificial systems) and 2) a natural system, which is a set of elements that arise naturally, without human construction. Both types of systems are coupled, that is, human systems interact with natural systems and vice versa in multi-levels and aspects.
There are several kinds of human-made systems (e.g., urban systems, economic systems, judicial systems) and natural systems. An urban system is a human-made system placed in a specific space and exists at a specific time. It is composed of essential parts, which are Resource and Population. A Resource is an essential part of one or more urban systems, for instance, a river can be a resource for different countries, and different cities. The resource is subcategorized as Urban Infrastructure and Agent as a Resource. |
||
|
|
According
to standard ISO/IEC 15288:2015, a system element is a discrete
part of a system. A system element can be hardware, software, data,
humans, processes, procedures (e.g., operator instructions), facilities,
materials, and naturally occurring entities (e.g., water, organisms,
minerals), or any combination. |
||
|
|
Urban infrastructure is a mix of structures built horizontally or vertically by humans, which provide a variety of utilities and services such as housing, transportation, and leisure. The design of these structures serves to ensure accessibility and convenience to meet the needs of the urban dwellers. |
||
|
|
Urban infrastructure is a mix of structures built horizontally or vertically by humans at risk. |
||
|
|
An Urban System is a human-made system placed in a specific space and time. It is composed of essential parts, which are Infrastructure, Geosphere, and Population. Population is a collective of agents who live or use the urban space and the tangible Infrastructure (hard infrastructure) through services (soft infrastructure). In turn, the Urban Space (Geosphere) is the territory, the place where the population (resident or non-resident) lives or uses the soil as well as where the infrastructure is located. |
||
|
|
An urban system is a set of interconnected parts (population, urban space, and infrastructure). An urban system at risk has one or more parts vulnerable or exposed to certain risk drivers in certain situations. |
||