|
|
|
Human Population : Class (in Ontology of Population / Ontology of Agents in Urban Systems / Ontology of Soft Infrastructure / Ontology Transport Service)
Class Diagram - Ontology of Agents in Urban Systems
![]() link
link
| Jump to: |
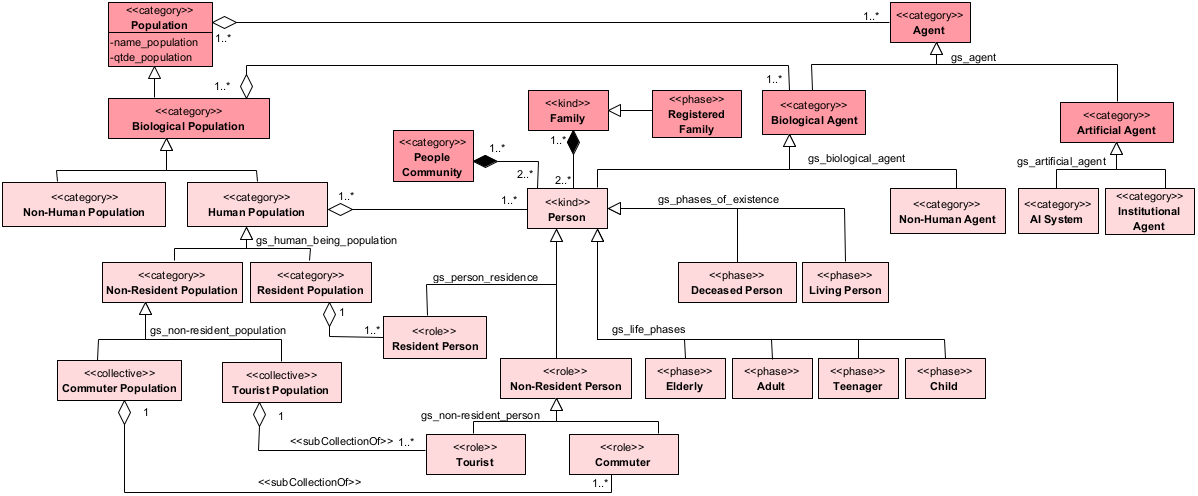
|
| Model Elements |
| Name | Description | ||
|
|
It is a phase or stage of human development that occurs after the stage of adolescence and puberty. There are three distinct stages: early (ages 19 to 45), middle (ages 45 to 60), and late (the later years thereafter).
There is no consensus about the starting age for these three stages of adulthood. The stages used here are extracted at https://psychologydictionary.org/adulthood/
However, the Italian population statistics by age group are arranged as follows at https://www.statista.com/statistics/789270/population-in-italy-by-age-group/ |
||
|
|
Any agentive Object, either physical (e.g. a person, a robot, an oak), or social (e.g. a corporation, an institution, a community). Defined by: https://w3id.org/italia/onto/l0 |
||
|
|
‘AI system’ means a machine-based system that is designed to operate with
varying levels of autonomy and that may exhibit adaptiveness after
deployment, and that, for explicit or implicit objectives, infers, from
the input it receives, how to generate outputs such as predictions,
content, recommendations, or decisions that can influence physical or
virtual environments.
Source: EU Artificial Intelligence Act. https://artificialintelligenceact.eu/article/3/ |
||
|
|
Artificial agent is a broad concept that encompasses both technological agents (AI systems, for example, robots, etc.) and agents socially built to act in social reality (e.g., companies, public entities with legal personality, etc.). |
||
|
|
A biological agent is a broad category that encompasses all biological agents present or potentially present in an urban system. These agents can have both a component role in the urban system and a risk driver role, actively participating in risk events initiated by hazardous situations. |
||
|
|
Biological Population is a group of biological organisms living in the same place at the same time. |
||
|
|
It is a human being between the stages of birth and puberty, or between the developmental period of infancy and puberty. It may also refer to an unborn human being.
For the UNICEF Convention, a child means every human being below the age of eighteen years unless under the law applicable to the child, the majority is attained earlier.
In the context of urban systems, the Child is a phase that a human being goes through. The following subphases are covered: Early childhood (birth to age 5), middle childhood (ages 6 to 12). |
||
|
|
A commuter is someone who travels a significant distance each day between home and place of work or study. | ||
|
|
It is a collective of people who regularly travel some distance to work or study. |
||
|
|
It is the phase in which a person is no longer alive. A person cannot be alive and not alive at the same time. Therefore, it is a disjointed phase from the Alive phase. |
||
|
|
"Elderly" is a concept that cannot be absolutely defined, as it has different meanings in different societies and historical periods. The United Nations refers to those aged 60 and over as "older persons", while ISTAT and the Ministry of Health speak of people aged 65 and over.
In 2018, during the National Congress of the Italian Society of Gerontology and Geriatrics (SIGG - Congresso Nazionale della Società Italiana di Gerontologia e Geriatria), an adjustment to 75 years was proposed. Given the increase in average life expectancy at birth (85 for women, 82 for men in Italy), SIGG argues for a distinction among people over 65 between those in the so-called third age (characterized by good health, social integration and access to resources) and those in the fourth age (characterized by dependence on others and physical decline).
In this ontology, the elderly are all people over the age of 65. |
||
|
|
1. A human community generally formed by people tied together by a relationship of coexistence, of kinship, of affinity, which constitutes the fundamental element of every society, since it is aimed, in its processes and relations, at the perpetuation of the species through reproduction.
2. A family is the basic unit in society traditionally consisting of two parents rearing their children (“Family.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary, Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/family.
3. A group of two or more persons related by birth, blood, marriage, de facto union, or adoption who live together.
4. All the descendants of a common ancestor. (Oxford Language) |
||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
It is a subtype of the Biological Population collective, covering the subtypes of resident, non-resident populations in a given space and at the same time. |
||
|
|
A juridical person is a legal person who is not a natural person but an
organization recognized by law as a fictitious person such as a
corporation, government agency, non-governmental organization, or
international organization (such as the European Union).
Juristic Person. An entity, such as a corporation, that is recognized as having legal personality, i.e. it is capable of enjoying and being subject to legal rights and duties. It is contrasted with a human being, who is referred to as a natural person. Source: https://www.oxfordreference.com/display/10.1093/oi/authority.20110803100027393 |
||
|
|
It is a phase or stage of being alive, as opposed to being dead, during which your organs work and carry out their functions. |
||
|
|
It is every non-human being with agentive capacity to influence an urban system. This category is classified as Pet, Plant, Wild Animal, Fungus, MGE, Virus, Mold, and Bacteria.
1) Pet is any domesticated or tamed animal that is kept as a companion and cared for affectionately.
2) Wild animal in a urban system is any non-domesticated animal that has adapted its lifestyle to living in the cities or in suburban neighborhoods.
3) A plant is a living and natural organism of the kind exemplified by trees, shrubs, herbs, grasses, ferns, and mosses, typically growing in a permanent site, absorbing water and inorganic substances through its roots, and synthesizing nutrients in its leaves by photosynthesis using the green pigment chlorophyll.
4) Mobile genetic element (MGE), also known as transposable element (TE), is a type of moving genetic material that can either move around within a genome or jump across different genomes.
5) Viruses may have arisen from mobile genetic elements that gained the ability to move between cells. They may be descendants of previously free-living organisms that adapted a parasitic replication strategy. Viruses can leave the cell and move to other cells and organisms; mobile genetic elements generally just move around the genome within a cell.
6) Fungus is any member of a kingdom of organisms called Fungi that lack chlorophyll, leaves, true stems, and roots, reproduce by spores, and live as saprotrophs or parasites. The group includes moulds, mildews, rusts, yeasts, and mushrooms.
7) A mold is a microscopic fungus that grows and lives on plant or animal matter or on non-organic objects. Most molds are made up of filaments and reproduce through the production of spores. Spores spread by air, water, or insects. There are many thousands of species of fungi. Mold is the colloquial term used for indoor fungi. Fungal spores occur naturally outdoors easily be transferred inside well they can sit on surfaces. Mold organisms are extremely resilient and have evolved to adapt to survive in sub-optimal conditions. Types of indoor mold differ according to geographical location. |
||
|
|
Non-Human Being Population is all populations that do not encompass human
beings but it is natural. It is subcategorized as: 2.1) Pet Population,
2.2) Wild Animal Population, 2.3) Plant Population, 2.4) Mobile Genetic
Element Population (MGE), 2.5) Fungus Population, 2.6) Protist Population,
and 2.7) Bacteria Population.
There is a subtype of MGE, which is the Virus Population. Also, there is a subtype of Protist Population, which is Mold Population. |
||
|
|
It is a role played by persons who are not registered in the Register of Residents in a given municipality at a given time. It can be a tourist or a person who temporarily lives in a certain place without having the rights and duties of residents. |
||
|
|
It is the collective of individuals who are not registered with the Registry of the Resident Population in a given municipality in a given time. It can be a tourist or a person who is temporally living in a particular place without the duties and rights of the residents. |
||
|
|
A group of people with diverse characteristics who are linked by social ties, share common perspectives and engage in joint action in geographical locations or settings. Community can be defined by a sense of identification with and emotional connection to others through common symbol systems, values, and norms; shared interests; and commitments to meeting mutual needs.
Source:https://www.evms.edu/education/resources/community-engaged_learning/glossary_of_terms/ |
||
|
|
It is every human being with the capacity to influence and act on an urban system. |
||
|
|
It is a collection of Agents (biological or artificial) of the same taxonomic class, counted or sampled at a given location or area, given a time interval. |
||
|
|
It is a group of people tied together by relationships of marriage, kinship, affinity, adoption, protection or affection.
Rule: The members must live and be habitually resident in the same municipality (Article 4 of Italian Presidential Decree 30/05/1989, n. 223) |
||
|
|
It is a person who is enlisted with the Resident Population
Registry in a particular local authority area in a given time. The
classification of a Resident Person as a <<role>> derives from residency
being an incidental characteristic of a human being. |
||
|
|
It refers to the collective of people enlisted with the Resident
Population Registry in a particular local authority area in a given
time. The classification of a Resident Person as a <<role>> derives from
residency being an incidental characteristic of a human being. |
||
|
|
It is the last phase of the childhood that a human being goes through (13 to 18 years). |
||
|
|
It is a role played by a person who is traveling or visiting a place for pleasure or interest. |
||
|
|
It is a collective of people who is traveling or visiting a place for pleasure or interesting. |
||