|
|
|
Soft Infrastructure : Class (in Ontology of Urban Infrastructure / Ontology of Urban System / Ontology of Soft Infrastructure)
Class Diagram - Ontology of Soft Infrastructure
![]() link
link
| Jump to: |
|
|
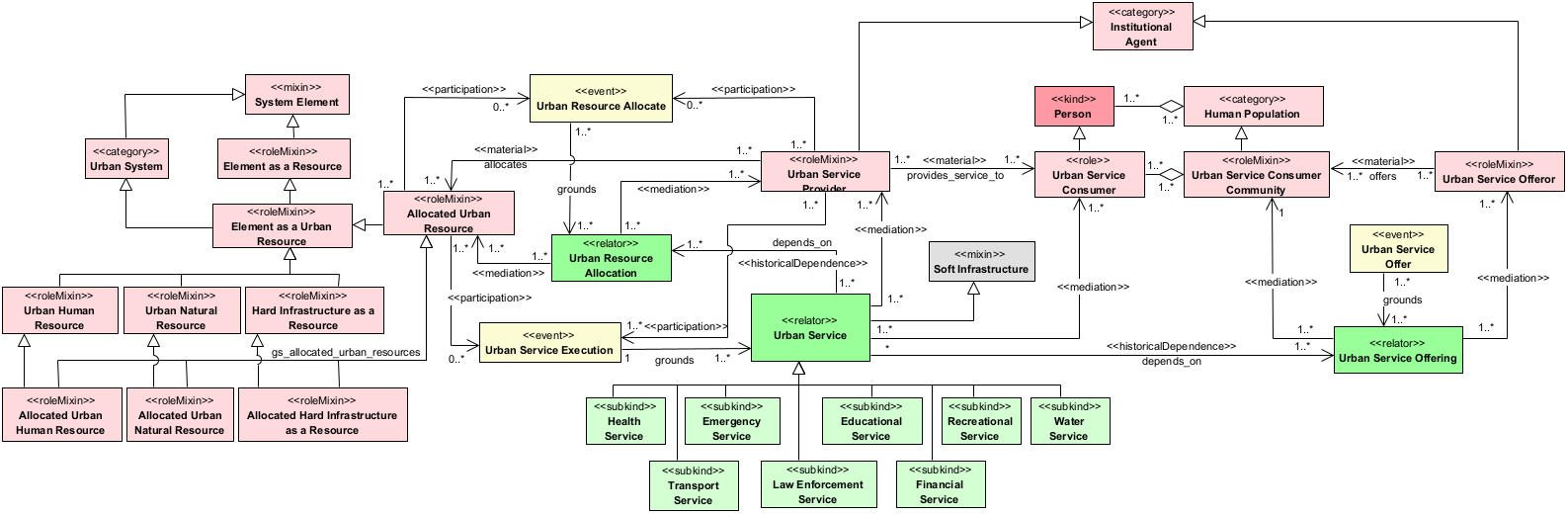
This diagram describes one of the components of Urban Infrastructure called Soft Infrastructure. Soft infrastructures include the set of relevant functions necessary for the ordinary and extraordinary management of the urban system, for instance, health, emergency, law enforcement, mid-term services (e.g., waste management), and long-term services including educational and recreational. |
| Model Elements |
| Name | Description | ||
|
|
It is a hard infrainstructure asset (e.g., bridge, road, street) allocated in a service provided in the context of urban system. |
||
|
|
It is a person or a set of people allocated in a service provided in the context of urban system. |
||
|
|
It is a natural asset (e.g., river, sea, lake, soil, sky) allocated in a service provided in the context of urban system. |
||
|
|
Allocated resources as a Service (RaaS). |
||
|
|
It is a service relation between the consumer of educational services and the agent who provides it. For instance, the public educational service provided by a public entity to people in a city. |
||
|
|
It
is everything that is used to satisfy the human needs. |
||
|
|
It
is every element that is used to satisfy the human needs in the context
of urban systems. |
||
|
|
It is a service relation between the consumer of emergency services and the agent who provides it. For instance, the public emergency service provided by a public entity to people in a city. |
||
|
|
It is a service relation between the consumer of the financial system and the agent who provides it. For instance, the financial system (e.g., banks) provided by a public entity to people in a city. |
||
|
|
|||
|
|
It is the tangible infrastructure, i.e. the physical infrastructure of roads, bridges, tunnels, railways, ports, etc., that are managed as assets in the context of an urban system. |
||
|
|
It is a service relation between the consumer of health services and the agent who provides it. For instance, the public health service provided by a public entity to people in a city. |
||
|
|
It is a subtype of the Biological Population collective, covering the subtypes of resident, non-resident populations in a given space and at the same time. |
||
|
|
A juridical person is a legal person who is not a natural person but an
organization recognized by law as a fictitious person such as a
corporation, government agency, non-governmental organization, or
international organization (such as the European Union).
Juristic Person. An entity, such as a corporation, that is recognized as having legal personality, i.e. it is capable of enjoying and being subject to legal rights and duties. It is contrasted with a human being, who is referred to as a natural person. Source: https://www.oxfordreference.com/display/10.1093/oi/authority.20110803100027393 |
||
|
|
It is a service relation between the consumer of law enforcement services and the agent who provides it. For instance, the legal system (courts, mediation courts, policy, etc) provided by a public entity to people in a city. |
||
|
|
It is every human being with the capacity to influence and act on an urban system. |
||
|
|
It is a service relation between the consumer of recreational services and the agent who provides it. For instance, the public recreational service provided by a public entity to people in a city. |
||
|
|
Soft infrastructure refers to the intangible things needed to maintain or improve the utilities and services such as financial, health, cultural, and social in an urban system. The population uses the infrastructure of an urban system through services offered by public or private agents. | ||
|
|
According
to standard ISO/IEC 15288:2015, a system element is a discrete
part of a system. A system element can be hardware, software, data,
humans, processes, procedures (e.g., operator instructions), facilities,
materials, and naturally occurring entities (e.g., water, organisms,
minerals), or any combination. |
||
|
|
It is a service relation between the consumer of transport services and the agent who provides it. For instance, the public transport service provided by a public entity to people in a city. |
||
|
|
Urban human resources is the set of people who make up the workforce of an urban system. |
||
|
|
Urban natural resource is a set of any biological, mineral, or aesthetic asset afforded by nature without human intervention that can be used for some form of benefit, whether material (economic) or immaterial. What is considered a “resource” (or, for that matter, “natural”) has varied over time and from one society to another. Examples of assets that can be considered natural resources include forests, surface water and groundwater, and the fertile lands or the soil and minerals within them (rather than the crops that grow on them), as well as energy resources (such as petroleum, natural gas, and heated water [that is, geothermal energy]) contained within layers of rock.
Source: https://www.britannica.com/science/natural-resource |
||
|
|
It is an event that allocates resources (human, natural or hard infrastructure resources) to provide a service in the context of an urban system. In this event participates an agent playing the role of Urban Service Provider as well as the resource to be allocated. This event creates the historical foundational of a relationship called Urban Resource Allocation between the allocated urban resource and the Urban Service Provider. |
||
|
|
It is the (reified) relationship between the Allocated Urban Resource and Urban Service Provider grounded by the Urban Resource Allocate event. |
||
|
|
It represents all services provided by a municipality, either directly or by contract, to any of its current residents. For example: sanitation, water, fire protection, parks, open space, recreation, and streets, roads, and mass transit. The Return Project views urban services as a relationship between the service consumer and the service provider in urban systems. This relation is usually formalized in a document (Normative Description) called Service Contract |
||
|
|
In general, a service consumer can be anything from a system, to an application, to an artificial agent, to a person. A service consumer is a user of products and services provided by a service provider, which can be either a company or a person. In the domain represented by urban systems, we restrict the definition of service consumer to people and service provider to companies (Juridical Person). Between a service consumer and a service provider, a contract is signed and establishes a bind (a service contract) based on legal rules for the consumption of services. |
||
|
|
It is a group of people connected by their shared interest in a service provided in a urban system. |
||
|
|
It is an event that executes a service in the context of urban system (health, transport, education). In this event participates one or more allocated urban resources and an agent (Juridical Person), playing the role of Urban Service Provider. This event creates the historical foundational of a relationship called Urban Service between the allocated urban resource and the Urban Service Provider. |
||
|
|
It is an event that offer a service in the context of urban system such as health, transport, education (dynamic aspect). In this event participates one Urban Service Consumer Community and one or more agents (Juridical Person), playing the role of Urban Service Offeror. This event creates the historical foundational of a relationship called Urban Service Offering between Urban Service Consumer Community and the Urban Service Offeror. |
||
|
|
It represents the relation between Urban Service Consumer Community and Urban Service Offeror. This relation is usually presented through oral or written publicity that binds the Service Offeror. |
||
|
|
It is a role plays by a Juridical Person in a relationship with the Urban Service Consumer Community. In this relation, Juridical Person offers a set of urban services for a group of people in an urban system. |
||
|
|
It is a role play by a Juridical Person who is active in service relationships with Urban Resources or Urban Service Consumer/Community. In this role, a Service Provider has the scope to offer, provide, and run urban services such as health, transportation, etc. |
||
|
|
An Urban System is a human-made system placed in a specific space and time. It is composed of essential parts, which are Infrastructure, Geosphere, and Population. Population is a collective of agents who live or use the urban space and the tangible Infrastructure (hard infrastructure) through services (soft infrastructure). In turn, the Urban Space (Geosphere) is the territory, the place where the population (resident or non-resident) lives or uses the soil as well as where the infrastructure is located. |
||
|
|
It is a service relation between the consumer of water services and the agent who provides it. For instance, the public water service provided by a public entity to people in a city. |
||